Japan’s work culture is renowned for its unique characteristics and traditions that set it apart from the rest of the world. With a reputation for diligence, dedication, and long working hours, Japanese work culture can be both fascinating and daunting. This article explores various aspects of Japan’s work culture, including its history, core values, challenges, and the ongoing efforts to reform and improve it.
Historical Context of Japanese Work Culture

Post-War Economic Boom
Following World War II, Japan experienced an economic miracle that transformed it into a global economic powerhouse. This period of rapid growth was fueled by an industrious workforce, a strong sense of community, and a national drive to rebuild and excel. The work culture that emerged during this time emphasized loyalty, hard work, and collective success.
Lifetime Employment
The concept of lifetime employment became a hallmark of Japanese companies during the post-war period. Employees would often remain with a single company for their entire career, fostering a strong sense of loyalty and stability. This system encouraged workers to invest deeply in their roles, knowing their company would reciprocate with job security and benefits.
Core Values in Japanese Work Culture
Dedication and Diligence
Japanese employees are known for their dedication and diligence. Long working hours are commonplace, and it is not unusual for employees to put in overtime without additional pay. This commitment is driven by a cultural expectation to contribute fully to the company’s success.
Collectivism and Teamwork

Teamwork is a fundamental aspect of Japanese work culture. The success of the group is prioritized over individual achievements, fostering a collaborative environment. This collectivist mindset is reflected in the common practice of group decision-making, where consensus is sought before making significant decisions.
Respect and Hierarchy
Respect for hierarchy and seniority is deeply ingrained in Japanese work culture. Employees are expected to show deference to their superiors and adhere to established protocols. This respect extends to communication styles, where indirect and polite language is often used to maintain harmony and avoid confrontation.
Typical Workday in Japan
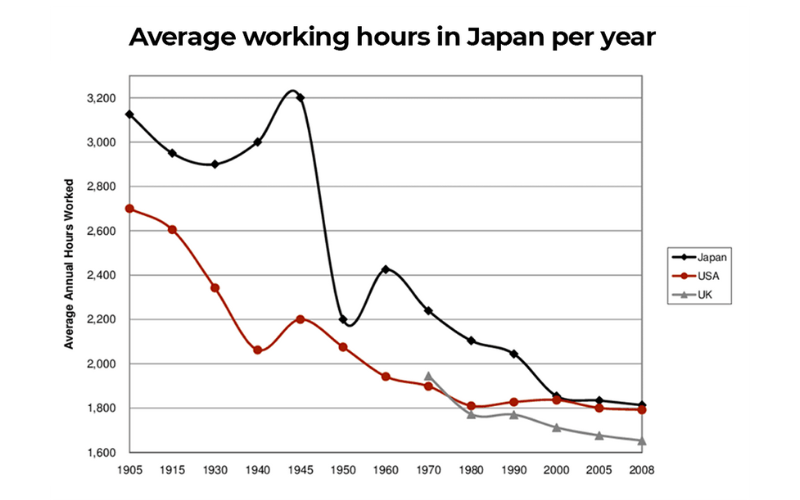
Working Hours
A typical workday in Japan starts around 9 AM and ends around 6 PM. However, it is common for employees to stay late into the evening, working extra hours to complete tasks. The concept of “karoshi,” or death by overwork, highlights the extreme end of this dedication to long hours.
Morning Meetings
Morning meetings, known as “chorei,” are a daily ritual in many Japanese companies. These brief sessions allow teams to align on priorities, share updates, and set the tone for the day. They reinforce the sense of teamwork and collective effort.
After-Work Socializing
Socializing with colleagues after work is a significant aspect of Japanese work culture. These gatherings, often at izakayas (Japanese pubs), provide an opportunity for employees to bond, discuss work informally, and build stronger relationships outside the office environment.
Challenges in Japanese Work Culture

Work-Life Balance
One of the most significant challenges in Japanese work culture is the lack of work-life balance. Long working hours and the expectation to socialize with colleagues after work can leave little time for personal life and family. This imbalance has led to increased stress and health issues among employees.
Gender Inequality
Gender inequality remains a persistent issue in Japanese work culture. Women often face barriers to career advancement and are underrepresented in leadership positions. Traditional gender roles and expectations contribute to this disparity, making it challenging for women to balance work and family responsibilities.
Mental Health Concerns
The intense pressure to perform and the long working hours can take a toll on employees’ mental health. Issues such as anxiety, depression, and burnout are prevalent. Despite growing awareness, mental health remains a stigmatized topic, and employees may hesitate to seek help.
Efforts to Reform Japanese Work Culture

Government Initiatives
In recent years, the Japanese government has recognized the need for work culture reform and introduced various initiatives to address these issues. Policies promoting work-life balance, such as limiting overtime hours and encouraging flexible work arrangements, are being implemented to improve the quality of life for workers.
Corporate Changes
Many Japanese companies are also taking steps to reform their work culture. Initiatives such as telecommuting, reduced working hours, and increased emphasis on mental health support are becoming more common. These changes aim to create a healthier and more sustainable work environment.
Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
Efforts to promote diversity and inclusion are gaining traction in Japan. Companies are recognizing the value of a diverse workforce and are taking steps to create more inclusive workplaces. This includes supporting women in leadership roles, accommodating employees with disabilities, and fostering a culture of respect and equality.
The Future of Japanese Work Culture
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of Japanese work culture. Automation, artificial intelligence, and remote work technologies have the potential to reduce the burden on employees and create more flexible work environments. Embracing these innovations can lead to increased productivity and improved work-life balance.
Changing Attitudes
Younger generations in Japan are challenging traditional work culture norms and advocating for change. Millennials and Generation Z employees prioritize work-life balance, mental health, and meaningful work. Their demands for a healthier and more fulfilling work environment are driving shifts in corporate practices and policies.
Global Influence
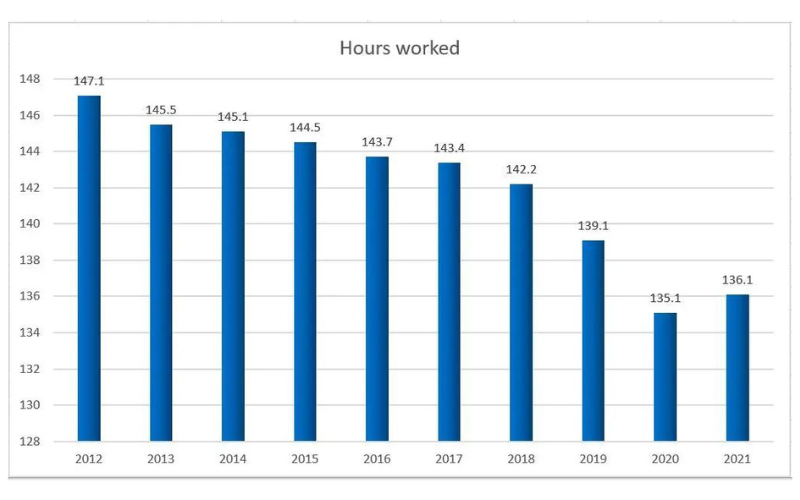
Globalization and increased interaction with international business practices are also influencing Japanese work culture. Exposure to different work cultures and values is encouraging Japanese companies to adopt more progressive approaches. This cross-cultural exchange is fostering a more open and adaptable work environment.
Conclusion
Japanese work culture is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has evolved over decades. While it is characterized by dedication, diligence, and teamwork, it also faces significant challenges related to work-life balance, gender inequality, and mental health. Ongoing efforts by the government, corporations, and individuals are driving positive changes, paving the way for a more balanced and inclusive future. By embracing technological advancements, changing attitudes, and global influences, Japan’s work culture is poised for transformation and growth.
FAQs
1. What is the concept of “karoshi” in Japanese work culture?
Karoshi, which translates to “death by overwork,” is a phenomenon in Japan where employees suffer from severe health issues or even death due to excessive working hours and stress. It highlights the extreme dedication and pressure faced by some workers in Japanese companies.
2. How do morning meetings, or “chorei,” contribute to Japanese work culture?
Chorei, or morning meetings, are a daily practice in many Japanese companies. These meetings help align team priorities, share updates, and foster a sense of teamwork and collective effort, setting a positive tone for the day.
3. What steps are being taken to address gender inequality in Japanese work culture?
Efforts to address gender inequality in Japanese work culture include promoting diversity and inclusion, supporting women in leadership roles, and encouraging policies that help balance work and family responsibilities. Both government initiatives and corporate changes are driving these efforts.
4. How is the Japanese government promoting work-life balance?
The Japanese government is promoting work-life balance through policies that limit overtime hours, encourage flexible work arrangements, and support initiatives aimed at improving the quality of life for workers. These measures are part of broader efforts to reform Japan’s work culture.
5. How are technological advancements influencing Japanese work culture?
Technological advancements, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and remote work technologies, are influencing Japanese work culture by reducing the burden on employees, increasing productivity, and creating more flexible work environments. Embracing these innovations is key to future work culture transformation.